Docker
1. What is Docker, and how does it differ from a virtual machine?
- Docker: Containeriation platform that packages applications and their dependencies into lightweight containers.
- Unlike VM, which include a full OS and emulate hardware using a hypervisor, Docker containers share the host's OS kernel, making them faster, and more resources efficient.
- Containers enable consistent environments across development, testing, and production.
2. What is a Docker image, and how is it different from a Docker container?
- Docker Image
- Template for create Docker containers.
- Include everything needed to run an application, including libraries, configuration, and dependencies.
- Docker Container
- Instance of a Docker image.
- Isolated and self-contained environment where your application can run without conflicts with other software on the host system.
3. Explain the Docker architecture and its main components.
- Docker’s architecture follows a client-server model. The main components are:
- Docker Client: Sends commands (e.g., docker run) to the Docker Daemon via CLI or API.
- Docker Daemon: Runs on the host, managing images, containers, networks, and storage.
- Docker Images: Templates for creating containers, stored locally or in registries.
- Containers: Runnable instances of images.
- Docker Registry: Stores and distributes Docker images.
4. What is a Dockerfile, and what are some common instructions used in it?
- Dockerfile is a script with instruction to build a Docker image.
FROM: Set the base image, e.g., `FROMRUN: Execute commands during building, e.g.,COPY: Copy files from the host to the container, e.g.,CMD: Set the command to run when the container starts, e.g.,EXPOSE: Publish a container's port to the host, e.g.,
Dockerfile in Spring Boot Application
FROM nexus.xxxx.com:8443/repository/xxxx-docker-release/openjre-21:1.0-0
COPY target/app.jar /app/app.jar
COPY config /app/config
ENTRYPOINT ["summon", "-f", "/etc/summon/secrets.yml", "java", "-jar", "/app/app.jar"]
EXPOSE 8080
5. How do you manage persistent data in Docker containers?
6. What is Docker Compose, and when would you use it?
- A tool for defining and running multi-container Docker applications using YAML file.
- It specifics servicem, network, and volumes.
- Run with command
docker-compose up - Normally use it in development environment.
7. How do you optimize a Docker image for production?
- Use a minimal base image, like
alpine, to reduce size. - Minimize layers by combining commands into a single layer, like
RUN apt-get update && apt-get install. - Remove unnecessary files and folders, like
/tmp,/var/tmp,/var/log,/var/cache. - Scan images for vulnerabilities using a tool like
docker scan.
8. What are Docker networks, and what are the different types?
- Enable communication between containers and host in Docker network.
- The main types are:
- Bridge: Default network, isolates containers on a private network with port mapping.
- Host: Containers share the host's network stack, removing isolation for better performance.
- Overlay: Enables communication across multiple hosts, used in Docker Swarm for distributed apps.
- None: Disables networking for isolated containers.
- For instance, could use bridge network to connect frontend and backend container on the same host.
9. How do you handle security in Docker?
- Run containers as non-root users by setting
USERin the Dockerfile. - Limit container privileges with --cap-drop or seccomp profiles.
10. How would you troubleshoot a container that fails to start?
- Check logs with
docker logs <container_id>to identify errors, like missing dependencies. - Inspect the container’s state with
docker inspect <container_id>to verify configuration, such as ports or volumes. - Confirm resource availability, like memory or disk space, using docker info.
11. Common Docker command.
- Container:
docker run -d -p 8080:80 <image_name>: Run the image in detached mode and mapping port 8080 to port 80.docker ps -a: List all conatiner include stopped.docker stop <container_name>docker start <container_name>dokcer restart <container_name>docker rm <container_name>docker exec -it <container_name> /bin/bash: Execute a command in a running container,-itmeans interactive mode.docker logs <container_name>: View the logs of a container.
- Image:
docker pull ubuntu:20.04docker build -t my_app:1.0docker imagesdocker rmidocker tag my_app:1.0 my_app:latestdocker push my_app:1.0
- Network & Volume:
docker network lsdocker network create my_networkdocker volume ls: Display available volume for persistent storage.docker volume create my_volume: Create a new volume.
- Docker Compose
docker-compose up -ddocker-compose down: Cleans up all resources created bydocker-compose up.
- System & Info.
docker infodocker versiondocker system prune -a: Removes unused containers, networks, images, and build cache.
- Troubleshooting & Inspection
docker inspect my_containerdocker stats: Displays real-time resource usage statistics for all running containers.
12. Flow to build container.
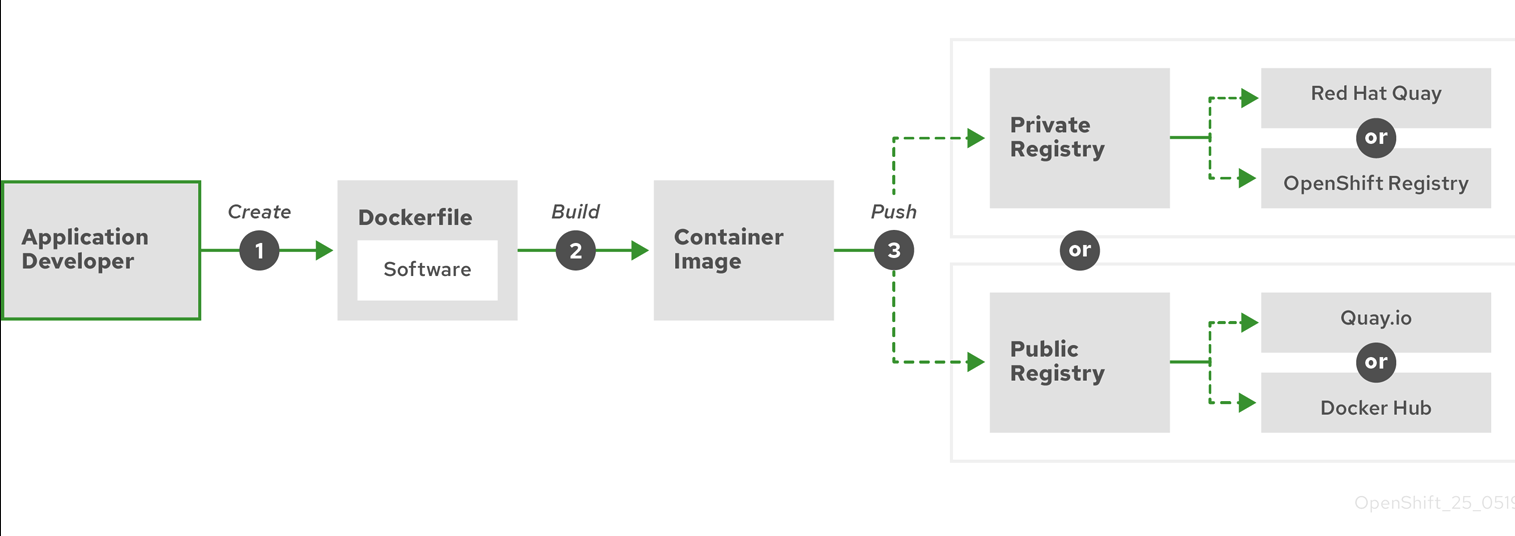
- Create Dockerfile in project root directory.
- To state the base image, expose ports.
- Run
docker build -t <image_name> . - Tag and push to registry.
docker push
- Pull and run the image by
docker run
13. docker run example
docker run --name mysql-primary -d \
--network mysql-net \
-e MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD=root_password \
-v mysql-primary-data:/var/lib/mysql \
-p 3306:3306 \
mysql:8.0
-e: Set environment variables.-v: Mount a volume.
13. Dockerfile vs Docker Compose
-
Dockerfile
- For building images.
docker build
-
docker-compose.yml
- For multi-container applications.
- Use
docker-compose up - Like link the web app with database container.