Two-Pointer (Linked List)
1. LeetCode 21. Merge Two Sorted Lists
- https://leetcode.com/problems/merge-two-sorted-lists/
- Use dummy node
Important
dummy node, no need to handle null pointer
use when you need to return a new linked list
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode list1, ListNode list2) {
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode p = dummy;
...
return dummy.next;
}
2. LeetCode 86. Partition List
- https://leetcode.com/problems/partition-list/
- Merging two in-ordered linkedlist
public ListNode partition(ListNode head, int x) {
// to store Node < x
ListNode dummy1 = new ListNode(-1);
// to store Node >= x
ListNode dummy2 = new ListNode(-1);
// p1 and p2 for returning the result
ListNode p1 = dummy1, p2 = dummy2;
ListNode p = head;
while (p != null) {
if (p.val >= x) {
p2.next = p;
p2 = p2.next;
} else {
p1.next = p;
p1 = p1.next;
}
// to break up the remaining nodes in p
ListNode temp = p.next;
p.next = null;
p = temp;
}
p1.next = dummy2.next;
return dummy1.next;
}
Important
要將原linked list的node斷關
3. LeetCode 23. Merge k Sorted Lists
public ListNode mergeKLists(ListNode[] lists) {
if (lists.length == 0) return null;
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode p = dummy;
// 创建一个优先级队列,将所有链表的头节点加入队列
PriorityQueue<ListNode> pq = new PriorityQueue<>(
lists.length, (a, b)->(a.val - b.val));
// 遍历队列,将队列中的Head加入链表
for (ListNode head : lists) {
if (head != null) {
pq.offer(head);
}
}
while (!pq.isEmpty()) {
ListNode node = pq.poll();
p.next = node;
if (node.next != null) {
pq.add(node.next);
}
p = p.next;
}
return dummy.next;
}
Important
Put all head nodes into a priority queue as min heap, so we can get the smallest node among all k lists. Time Complexity: O(Nlogk)
- In
pq, the size of queue is k, so the time complexity ofpoll()andadd()is O(logk). - All nodes are traversed once, so the time complexity of
whileloop is O(N).
4. LeetCode 19. Remove Nth Node From End of List
public ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) {
// 虚拟头结点
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1);
dummy.next = head;
// 删除倒数第 n 个,要先找倒数第 n + 1 个节点
ListNode x = findFromEnd(dummy, n + 1);
// 删掉倒数第 n 个节点
x.next = x.next.next;
return dummy.next;
}
private ListNode findFromEnd(ListNode head, int k) {
ListNode p1 = head;
// p1 先走 k 步
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
p1 = p1.next;
}
ListNode p2 = head;
// p1 和 p2 同时走 n - k 步
while (p1 != null) {
p2 = p2.next;
p1 = p1.next;
}
// p2 现在指向第 n - k + 1 个节点,即倒数第 k 个节点
return p2;
}
- If you want to delete the nth node from the end, you need to find the (n + 1)th node from the head
- The reason to use dummy head is to prevent null pointer.
- Let say we have a linked list: 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5, and you are required to delete the 5th node from the end.
- In this case, you need to find the 6th node from the head, which is not possible.
5. LeetCode 876. Middle of the Linked List
- https://leetcode.cn/problems/middle-of-the-linked-list/description/
- Slow pointer: move one step at a time
- Fast pointer: move two steps at a time
- Because
fastmoves twice as fast, whenfastreaches the end,slowwill be in the middle.
6. LeetCode 141. Linked List Cycle
- Use above technique
- Linked List with Ring: it does not end with
null - If fast pointer can reach the end of list(i.e.
null) -> the list has no cycle - If the fast pointer catches up the slow pointer (meet at the same node), it means the fast pointer has looped around in a cycle
public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {
// 快慢指针初始化指向 head
ListNode slow = head, fast = head;
// 快指针走到末尾时停止
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
// 慢指针走一步,快指针走两步
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
// 快慢指针相遇,说明含有环
if (slow == fast) {
return true;
}
}
// 不包含环
return false;
}
- LeetCode 142. Linked List Cycle
public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {
ListNode fast, slow;
fast = slow = head;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
if (fast == slow) break;
}
// 上面的代码类似 hasCycle 函数
if (fast == null || fast.next == null) {
// fast 遇到空指针说明没有环
return null;
}
// 重新指向头结点
slow = head;
// 快慢指针同步前进,相交点就是环起点
while (slow != fast) {
fast = fast.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
return slow;
}- Suppose the slow pointer has traveled k steps when fast and slow meet
- it means fast has traveled 2k steps
- the extra k step (2k - k) must be a multiple of the cycle's length
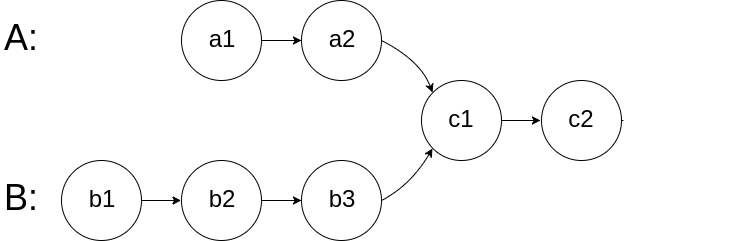
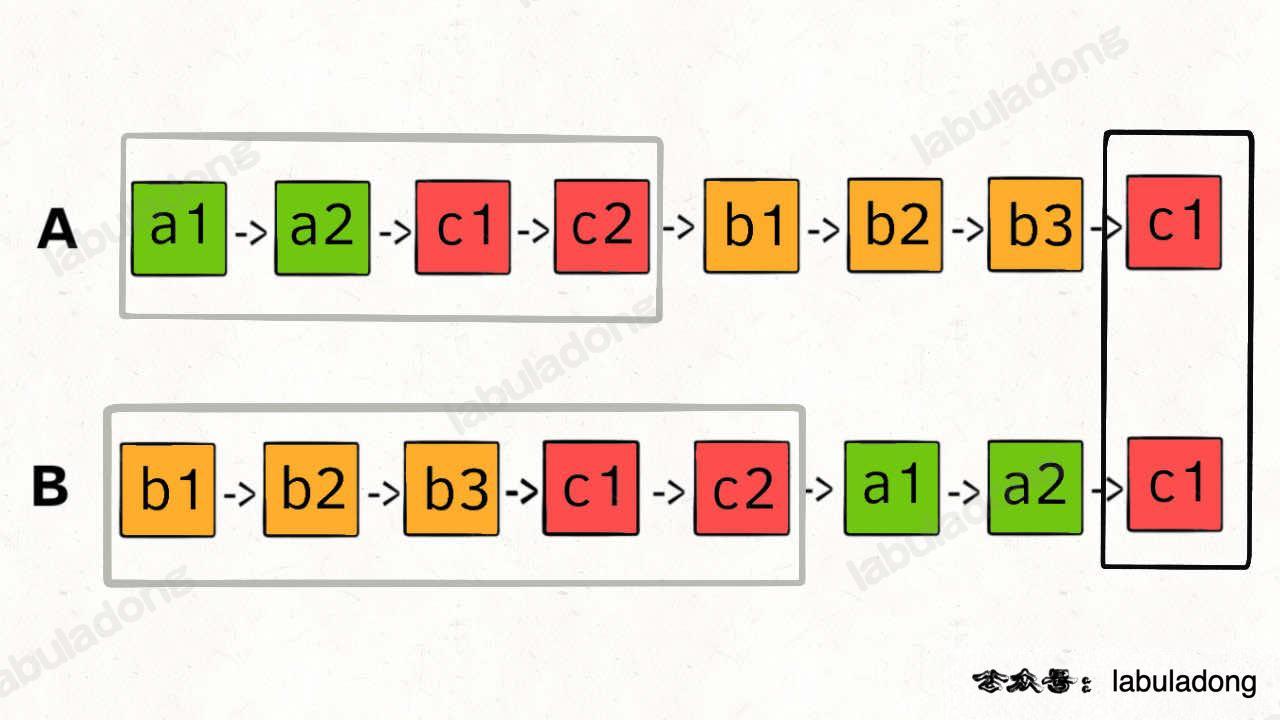
7. LeetCode 160. Intersection of Two Linked Lists
-
-
-
If no intersection exists, the two pointers will meet at the end of the list (null)
- A: a1 -> a2 -> c1 -> c2 -> b1 -> b2 -> b3 -> c3 -> c4 -> null
- B: b1 -> b2 -> b3 -> c3 -> c4 -> a1 -> a2 -> c1 -> c2 -> null
8. LeetCode 82. Remove Duplicates from Sorted List II
Idea
-
分解為two linked lists: 1) Unique List 2) Duplicated List
-
then return the head of unique list
-
what is duplicate?
- the value of current node == the value of next node
- the value of current node == the value of last node in duplicate list
Code
public ListNode deleteDuplicates(ListNode head) {
// / 运用虚拟头结点技巧,题目说了 node.val <= 100,所以用 101 作为虚拟头结点
ListNode dummyUniq = new ListNode(101);
ListNode dummyDup = new ListNode(101);
ListNode pUniq = dummyUniq, pDup = dummyDup;
ListNode p = head;
while (p != null) {
if ((p.next != null && p.val == p.next.val) || p.val == pDup.val) {
// 发现重复节点,接到重复链表后面
pDup.next = p;
pDup = pDup.next;
} else {
// 不是重复节点,接到不重复链表后面
pUniq.next = p;
pUniq = pUniq.next;
}
p = p.next;
// 将原链表和新链表断开
pUniq.next = null;
pDup.next = null;
}
return dummyUniq.next;
}
13. LeetCode 206. Reverse Linked List
- Reverse the direction of each node
- Initilization
pre = null:cur = head:nxt = head.next:
...
while (cur != null) {
cur.next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = nxt;
if (nxt != null) {
nxt = nxt.next;
}
}
...
14. LeetCode 445. Add Two Numbers II
- 不可用reverse linked list的方法
- instead, use Stack, FILO
- Then use method in 2. Add Two Numbers