Binary Search
I. Basic Binary Search
Step
- Use two points
leftandrightto reduce the serach range - Find the middle point
mid
Implementation
public int binarySearch(int[] nums, int target) {
int left = 0, right = nums.length - 1;
while (left <= right) {
int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
if (nums[mid] == target) {
return mid;
} else if (nums[mid] < target) {
left = mid + 1;
} else if (nums[mid] > target) {
right = mid - 1;
}
}
}
Why use left <= right instead of left < right?
rightisnums.length - 1, points to the last element in the array. Ifrightisnums.length,it would be index out of bound.- The former one is
[left, right],the later one is[left, right) - We here use the former one as the search range
- The termination condition of
left <= rightisleft = right + 1,e.g.[3, 2],區間為空 - The termination condition of
left < rightisleft = right,e.g.[3, 3],區間不為空- Special handling
// ...
while (left < right) {
// ...
}
return nums[left] == target ? left : -1;
- Special handling
Why left = mid + 1, right = mid - 1?
- Our search space is
[left, right] - When we find
nums[mid] != target, we go search in[left, mid - 1]or[mid + 1, right] - Because we already search
nums[mid], so we should remove it from search space
II. Left-Bounded Binary Search ([left, right))
Implementation
int left_bound(int[] nums, int target) {
int left = 0;
// 注意
int right = nums.length;
// 注意
while (left < right) {
int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
if (nums[mid] == target) {
right = mid;
} else if (nums[mid] < target) {
left = mid + 1;
} else if (nums[mid] > target) {
// 注意
right = mid;
}
}
return left;
}
Why use < instead of <=?
- As
right = nums.length, the search space in every iteration is[left, right) - The termination condition is
left == right, the search space is 0, e.g.[2, 2)
Why left = mid + 1 and right = mid?
- Our search space is
[left, right) - So after we check
nums[mid]and find it is not equal totarget, we go to the left side ofmidand right side of mid - go to the right side of
mid:[mid + 1, right) - go to the left side of
mid:[left, mid)
Why does this algorithm find the left boundary?
- It do not return the index of the target when we find the target
- Instead, we narrow the upper bound of the search space
if (nums[mid] == target) {
right = mid;
}
Why return left instead of right?
- Both are the same because the while loop ends when
left == right
III. Left-Bounded Binary Search ([left, right])
Implementation
int leftBound(int[] nums, int target) {
int left = 0, right = nums.length - 1;
while (left <= right) {
int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
if (nums[mid] < target) {
left = mid + 1;
} else if (nums[mid] > target) {
right = mid - 1;
} else if (nums[mid] == target) {
right = mid - 1;
}
}
if (left < 0 || left >= nums.length) {
return -1;
}
return nums[left] == target ? left : -1;
}
IV. Right-Bounded Binary Search ([left, right))
Implementation
int right_bound(int[] nums, int target) {
int left = 0, right = nums.length;
while (left < right) {
int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
if (nums[mid] == target) {
// 注意
left = mid + 1;
} else if (nums[mid] < target) {
left = mid + 1;
} else if (nums[mid] > target) {
right = mid;
}
}
// 注意
if (left - 1 < 0 || left - 1 >= nums.length) {
return -1;
}
return nums[left - 1] == target ? left - 1 : -1;
}
Why return left - 1?
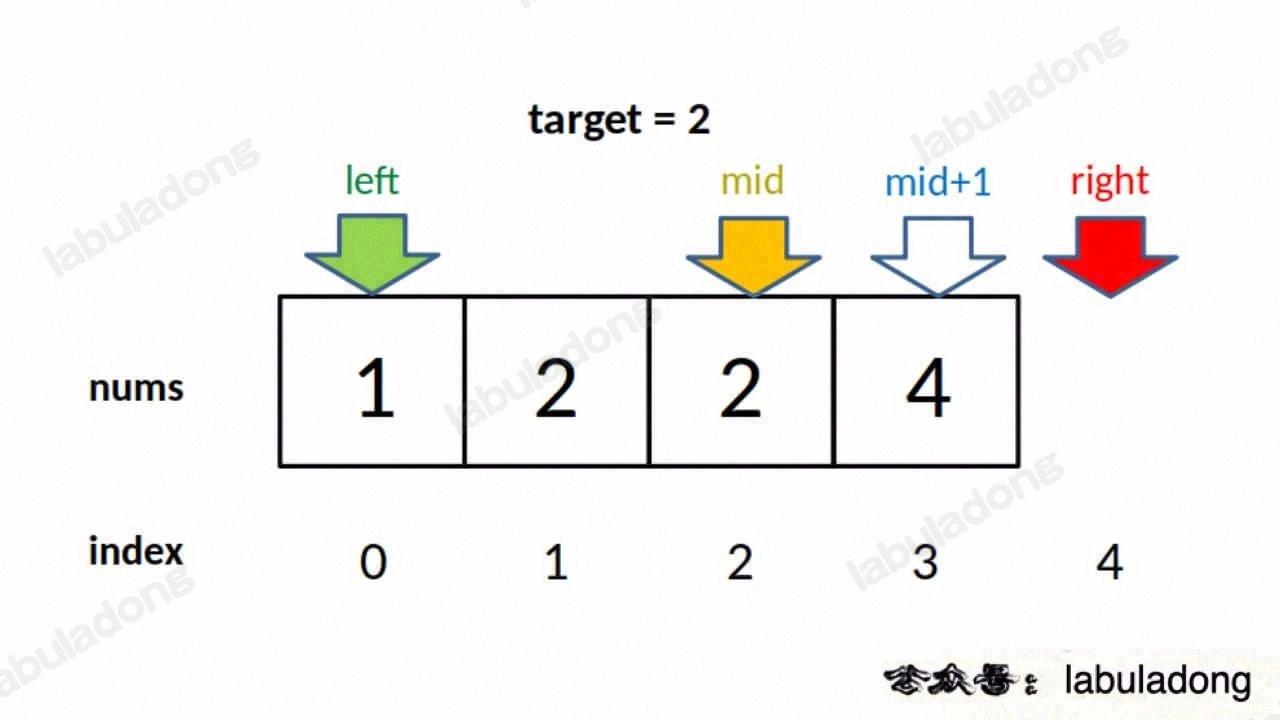
if (nums[mid] == target) {
left = mid + 1;
// think it as: mid = left - 1
}
- When the while loop end,
leftbecomemid + 1.nums[left]is the equal totarget(as in the image), andnums[left - 1]could be the target
Summary
1. Basic Binary Search
因为我们初始化 right = nums.length - 1
所以决定了我们的「搜索区间」是 [left, right]
所以决定了 while (left <= right)
同时也决定了 left = mid+1 和 right = mid-1
因为我们只需找到一个 target 的索引即可
所以当 nums[mid] == target 时可以立即返回
2. Left-Bounded Binary Search
因为我们初始化 right = nums.length
所以决定了我们的「搜索区间」是 [left, right)
所以决定了 while (left < right)
同时也决定了 left = mid + 1 和 right = mid
因为我们需找到 target 的最左侧索引
所以当 nums[mid] == target 时不要立即返回
而要收紧右侧边界以锁定左侧边界
3. Right-Bounded Binary Search
因为我们初始化 right = nums.length
所以决定了我们的「搜索区间」是 [left, right)
所以决定了 while (left < right)
同时也决定了 left = mid + 1 和 right = mid
因为我们需找到 target 的最右侧索引
所以当 nums[mid] == target 时不要立即返回
而要收紧左侧边界以锁定右侧边界
又因为收紧左侧边界时必须 left = mid + 1
所以最后无论返回 left 还是 right,必须减一