Basic
1. What are the three normal forms of a database?
-
First Normal Form (1NF)
-
Requires that each column in a database table contains indivisible atomic data items.
Student ID Name Family Information School Information 1 John Doe Parents: Mike, Jane School: XYZ High, Grade: A 2 Jane Smith Parents: Bob, Alice School: ABC High, Grade: B -
Here, the "Family Information" and "School Information" columns contain multiple pieces of data.
-
Adjusted Table (Satisfies 1NF):
Student ID Name Parent 1 Parent 2 School Name Grade 1 John Doe Mike Jane XYZ High A 2 Jane Smith Bob Alice ABC High B
-
-
Second Normal Form (2NF)
-
Eliminates partial dependencies.
-
Building on 1NF, non-key attributes must fully depend on the entire primary key (eliminating partial functional dependencies of non-key attributes on the primary key).
-
2NF ensures that every column in a database table is related to the entire primary key, not just a part of it (primarily relevant for composite primary keys).
-
Table: CourseEnrollments (Before 1NF)
StudentID CourseCode StudentName CourseName DepartmentName EnrollmentDate S001 C001 Alice Smith Databases Computer Science 2025-09-01 S001 C002 Alice Smith Calculus Mathematics 2025-09-03 S002 C002 Bob Jones Calculus Mathematics 2025-09-02 - Primary Key: (StudentID, CourseCode) (composite key, as a student can enroll in multiple courses, and a course can have multiple students).
- 2NF Violation: StudentName, CourseName, and DepartmentName depend on only part of the composite key, not the entire key (StudentID, CourseCode).
-
Adjusted Tables (Satisfy 2NF)
-
Split the table:
StudentID StudentName S001 Alice Smith S002 Bob Jones CourseCode CourseName DepartmentName C001 Databases Computer Science C002 Calculus Mathematics StudentID CourseCode EnrollmentDate S001 C001 2025-09-01 S002 C002 2025-09-02 S001 C002 2025-09-03
-
-
-
Third Normal Form (3NF):
-
Ensure non-key attributes depend only on the primary key, not other non-key attributes
EmployeeID EmployeeName DepartmentID DepartmentName DepartmentLocation E001 Alice Smith D01 Marketing New York E002 Bob Jones D02 Engineering San Francisco E003 Carol White D01 Marketing New York - Adjusting to 3NF
EmployeeID EmployeeName DepartmentID E001 Alice Smith D01 E002 Bob Jones D02 E003 Carol White D01 DepartmentID DepartmentName DepartmentLocation D01 Marketing New York D02 Engineering San Francisco
-
2. Table Joins in MySQL
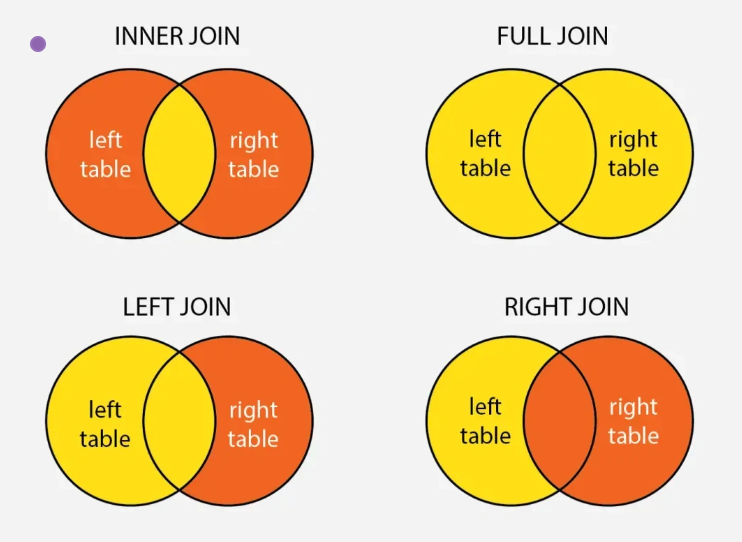
- Inner Join (INNER JOIN)
SELECT employees.name, departments.name
FROM employees
INNER JOIN departments
ON employees.department_id = departments.id;
- Left Outer Join (LEFT JOIN)
SELECT employees.name, departments.name
FROM employees
LEFT JOIN departments
ON employees.department_id = departments.id;
- Right Outer Join (RIGHT JOIN)
SELECT employees.name, departments.name
FROM employees
RIGHT JOIN departments
ON employees.department_id = departments.id;
- Full Outer Join (FULL JOIN)
- A full outer join returns all rows from both tables, including non-matching rows. In MySQL, FULL JOIN is not directly supported and must be implemented using
UNION. Example:
SELECT employees.name, departments.name
FROM employees
LEFT JOIN departments
ON employees.department_id = departments.id
UNION
SELECT employees.name, departments.name
FROM employees
RIGHT JOIN departments
ON employees.department_id = departments.id;