Binary Tree
Introduction
- The most important data structure.
- Many complex data structure are based on binary tree, such as RB-tree, Binary heaps, Graph, etc.
- It is not just a data structure, it represnets a recursive way of thinking. All recursive algorithms, such as Backtracking algorithm, BFS algorithm, Dynamic Programming (abstracted the problem into binary tree problem).
Common Types of Binary Tree
-
Full/Perfect Binary Tree
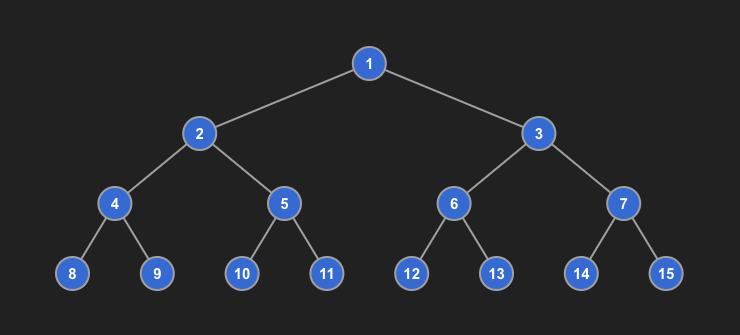
- Assuming the depth is
h, the total number of nodes is2^h - 1
-
Complete Binary Tree
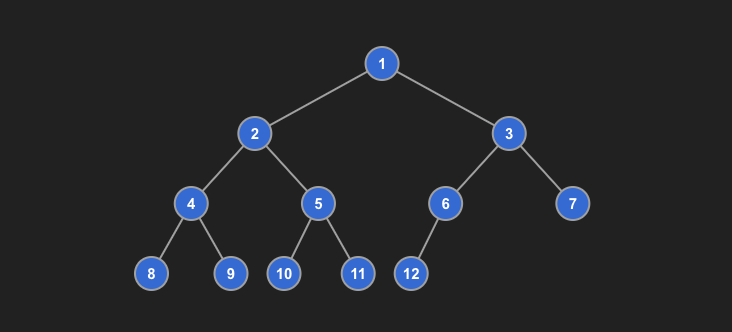
- Every level is filled from left to right, and except the last level.
-
Binary Search Tree
- For every node in the tree, all nodes in its left subtree are less than the node, and all nodes in its right subtree are greater than the node.
-
Height-Balanced Binary Tree
-
Height difference between the left and right subtrees of every node is no more than 1.
-
Example of height balanced binary tree
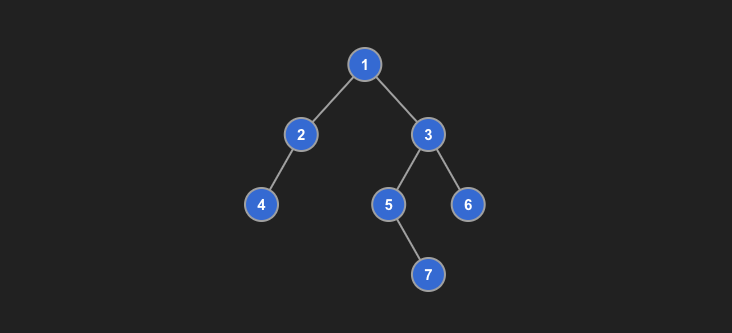
-
Example of NOT height balanced binary tree
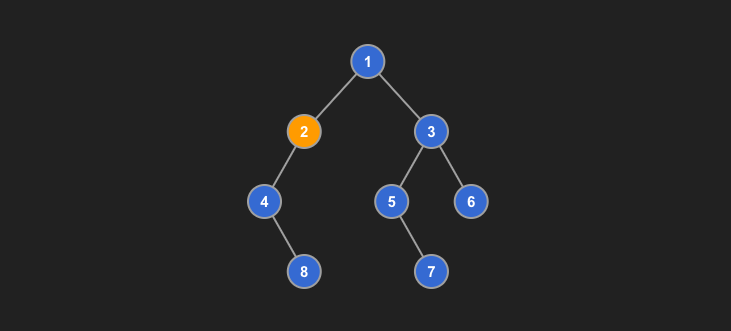
- As node 2 has a left subtree with height of 2 and right subtree with height of 0.
-
If a height-balanced tree has N nodes, the height of the tree will be
O(log N).
-
-
Self-Balancing Binary Tree
- Keep the height balanced while inserting and deleting is important as we want to keep the height to be
O(log N). - The key is to "rotate" the tree when the height is unbalanced.
- Keep the height balanced while inserting and deleting is important as we want to keep the height to be